Shell Script QA-Ao
*] to know the current shell
echo $0
echo $SHELL
*] $(hostname)
*] let
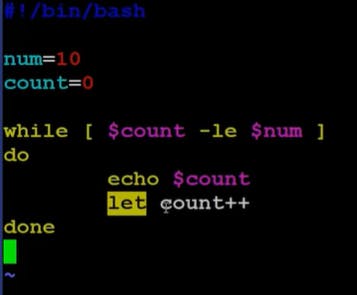
*]

*] ./<f_n>.sh
" . " represents current dir
if u want to specify path you can
*] Best practices in Shell Script
use comments
use proper naming convention for variables
make variable 'local' or 'readonly'
readonly -> value wont change after declaring
local -> it will be accessible only inside the function & it wont be accessible after that
use "" to indicate a string
exit with return code when something goes wrong -> exit 1
Consider option for "Logging", u can use "logger" in your script. You can find logs under "var/logs/messages" or u can redirect it into a file using ">>"
use condition to check whether requirement is checked or not
use functions to reuse a code
use Indentation
perform syntax check / dry run of your script -> bash -n <script_name>.sh
enable debugging of the script -> set -x
exit when script tries to use undeclared variables -> set -u, set -o nounset
make your script exit when a command fails -> set -e, set -o errexit
*]

*]
dos2unix <script_name>.sh
it converts the file to unix format
#to check for any errors (proper way of writing)
*] exit status
if used exit in shell script, then it returns the exit status value of its previous command, by dafault it returns the same exit code of its previous command
if we give a value infront of exit then it gives that value, exit 1
the exit status code is from 0 to 255
& if u give 256 then it will be considered as 0 & for 257 it will be 1 & it continues
USECASE:
if the condition is false in shell script then we don't want to move forward, at that time we use 'exit'
if we r performing some task for a user & we ask for user name, passwd and if that user doesn't even exist, then we want to terminate the script at that point itself
*]
shellcheck <script_name>.sh
*] why we get ++
when we use parenthesis i.e., "( )", then it will be executed in subshell so we get "++"
ex: for i in $(seq 1 3)
If u want to change the symbol "+" to something else then change the variable PS4
PS4="~"
now "+" will be converted to "~"
PS4='$LINENO:' --> for line no
*] Debugging in shell script
bash script doesn't have any built-in debugging tools but we can use external tools like shellcheck and bashdb for debugging & static code analysis of script
logging
we can redirect the output of the script to a file and we can use
loggercommand to log errors
use flags like
set -xfor debugging